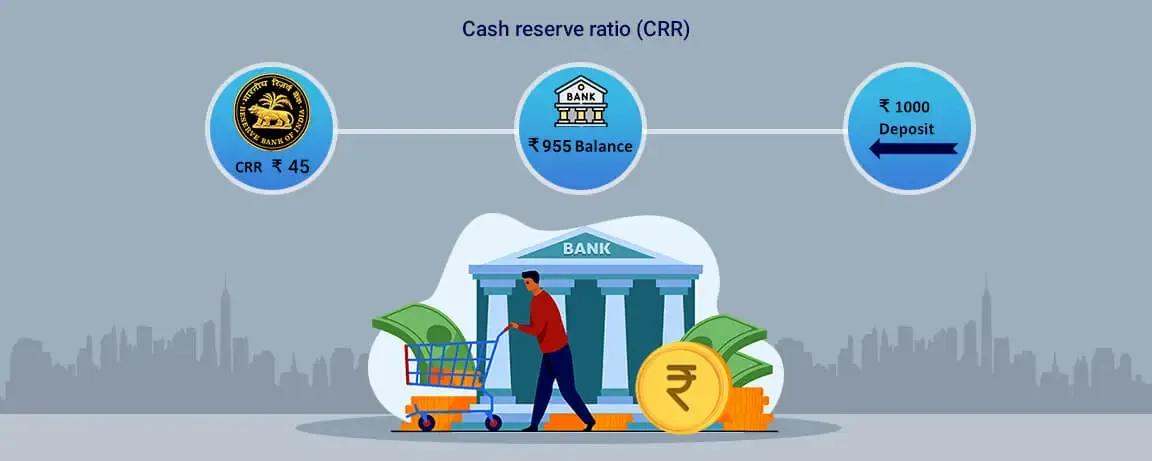
What is Cash Reserve Ratio & How It Works?
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is the percentage of the total deposits of a bank that it needs to maintain as liquid cash. It is a Reserve Bank of India (RBI) requirement and the RBI keeps the cash reserve. Banks do not earn any interest on this liquid cash that is maintained with the RBI and they also cannot use it for investment and lending purposes. The current CRR is 4.50 since May 21st 2022.
Here is everything you want to know about CRR.
What are the objectives of Cash Reserve Ratio?
The CRR acts as one of the reference rates while determining the base rate. Base rate is the minimum lending rate below which banks are not allowed to lend funds. This base rate is determined by the RBI. The CRR is fixed and it ensures transparency in borrowing and lending in the credit market. In addition to this, there are following two main objectives of CRR:
- CRR ensures that a portion of the bank’s deposit is with the RBI and is hence, secure.
- Another objective of Cash Reserve Ratio is to keep inflation under control. In the times of high inflation in the economy, Central Bank raises the Cash Reserve Ratio to reduce the quantum of money left with the banks to sanction loans. It controls the flow of money in the economy, thus reducing investments and bringing down inflation.
How does Cash Reserve Ratio work?
In case the RBI decides to increase the CRR, the amount of money available with the banks decreases. It is the RBI’s way of keeping the excess flow of money controlled in the economy. The cash balance to be maintained by the scheduled banks with the RBI should be at least 4% of the total Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL). This is done on a fortnightly basis.
NDTL includes deposits of the general public and the balance held by the banks with other banks. Demand deposits include all liabilities that the bank need to pay on demand such as demand drafts, current deposits, demand liabilities portion of savings bank deposits, and balances in overdue fixed deposits.
Time deposits include deposits that are to be repaid on maturity and where depositors cannot withdraw money immediately. Instead, they are required to wait for a certain period to gain access to their funds. This includes fixed deposit (FD), staff security deposits, and time liabilities portion of savings bank deposits.
The bank’s liabilities include call money market borrowings, investment in deposits and certificates of deposits in other banks. The higher the CRR, the lesser is the amount of money available with the banks for lending and investing.
Effects of CRR on the economy?
CRR is one of the key components of the RBI’s monetary policy that is used to regulate the money supply, inflation level and liquidity in the nation. The higher the CRR, the lower will be the liquidity with the banks and vice-versa. In the times of high inflation levels, RBI attempts to reduce the flow of money in the Indian economy and for this, RBI increases the CRR, resulting in reducing the loanable funds available with the banks. Doing this slows down investment and lowers the supply of money in the economy. This results in impacting the growth of the economy negatively. However, it also helps bringing down inflation.
When RBI wants to boost funds into the system, it lowers down the CRR, which increases the loanable funds available with the banks. In turn, the banks sanction a large number of loans to businesses and industries for different investment purposes. Doing this also boosts the overall supply of funds in the economy, which ultimately improves the growth rate of the economy.
Why is CRR changed regularly?
As per the guidelines of RBI, every bank has to maintain a ratio of its total deposits that can also be held with currency chests. It is considered to be the same as kept with the RBI. The RBI is free to change this ratio at regular intervals from time to time. When this ratio changes, it impacts the economy.
Banks make profits by lending. To pursue this goal, banks may lend out maximum amount for higher profits and would be left with very little cash with them. In the situation of an unexpected rush of withdrawing their deposits by customers, banks will be unable to meet all the repayment needs.
Due to this reason, CRR is crucial to ensure that there is always a specific part of all the deposits in every bank which is kept safe with them. CRR ensures liquidity against deposits along with controlling the interest rates in the economy.
FAQs
What is current CRR?
The current CRR is 4.50 since May 21st 2022.
What is current Base Rate?
The current base rate of the RBI is 7.25% to 8.80%.
Who calculates the base rate in India?
The RBI calculates the base rate in India.
What is current Repo Rate?
Since May 2020, the RBI's Repo rate is 4.40%.